Admin
Table of contents
- Managing User Permissions
- Managing Organizations
- Managing User Limits
- Excluding Models
- Excluding MCP Servers
- MCP Server Configuration
The Admin Panel is the Django Admin interface for the Aqueduct Gateway. It provides direct access to database objects and is used for advanced administrative actions, such as creating endpoints and models or managing user privileges.
Managing User Permissions
Admins can manage the permissions of other users through the Django Admin interface. User permissions are controlled using Django’s built-in groups. The main groups used in Aqueduct are:
userorg-adminadmin
To grant a user admin privileges, you must assign them to the admin group and ensure that both the “staff” and “superuser” flags are set to True in the Django Admin. If you wish to promote a user to org-admin, change their group from user to org-admin and remove the user group from their group list.
Team admins are managed differently: they are assigned through a many-to-many relationship between users and teams, which is handled in the Aqueduct UI. For more information, see the Teams page.
Managing Organizations
As an admin, you can assign yourself or other users to different organizations within the admin panel. This is useful if you need to administer multiple organizations. Organization assignments are managed within the user model in the admin interface, where the organization is presented as part or the user profile.
Note: Organization assignments made in the admin panel may be overwritten on the user’s next login, as user data is updated during authentication.
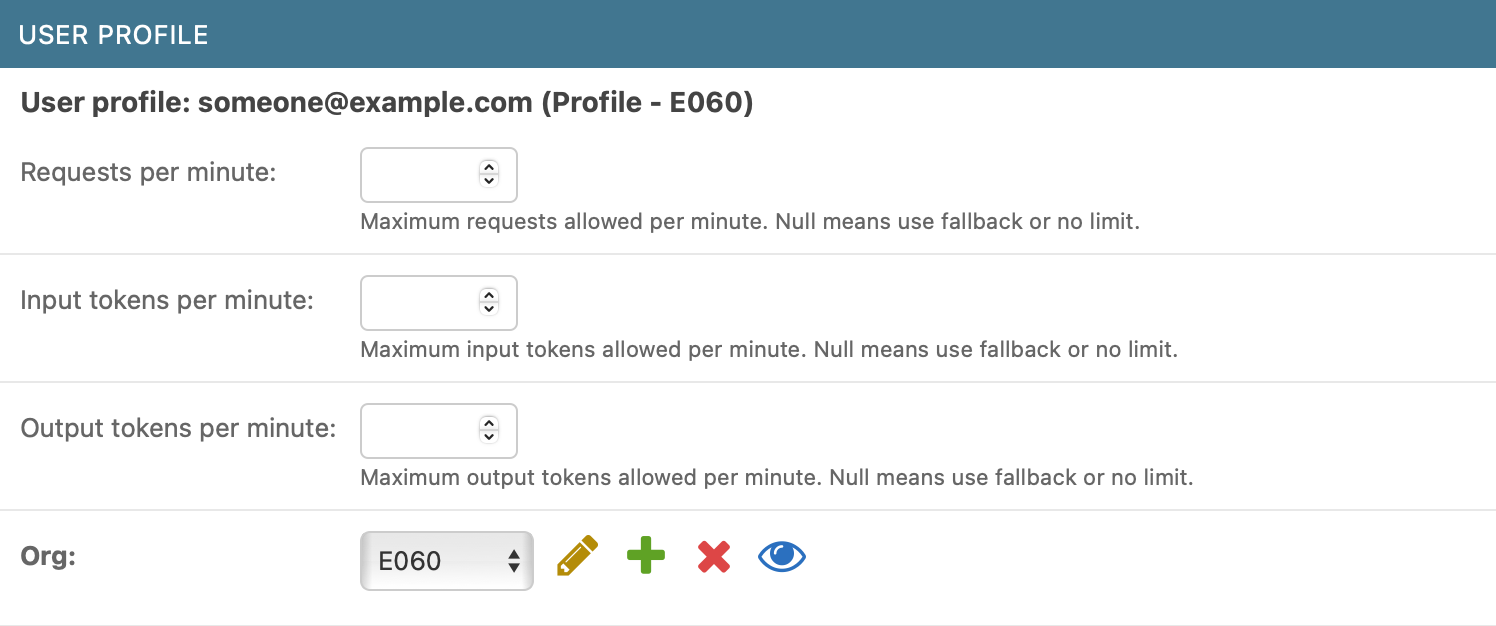
Managing User Limits
You can also change the request usage limits for individual users within the UserProfile inline model. This functionality is currently not available in the main UI and must be performed through the Django Admin interface.
Excluding Models
To exclude models for Orgs, Teams or specific UserProfiles, select the models to be excluded in the detail view admin interface of the specific entity. Excluded models are not available in any endpoints (returns 404) and are filtered from the model list.

Merge Exclusion Lists
The merge_exclusion_lists field determines how exclusion lists are built across the User, Team, Org, and global settings levels. When merge_exclusion_lists is enabled, the exclusion list for an entity is constructed by merging its own list with those from higher levels—moving upward through Org and finally the global settings. If merge_exclusion_lists is disabled at any level, merging stops there, and higher-level exclusions (including global) are not included.
Example:
Suppose a User has an exclusion list ["A", "B"] and merge_exclusion_lists=True; their Org has ["C"] with merge_exclusion_lists=False; and the global exclusion list is ["D"]. The effective exclusion list for the User would be ["A", "B", "C"]—the Org’s merge_exclusion_lists=False means the global settings are ignored.
This system provides fine-grained control over how and where model exclusions are inherited.
Excluding MCP Servers
Similar to model exclusions, you can exclude specific MCP servers for Organizations, Teams, or UserProfiles through the admin interface. This prevents users from accessing certain MCP servers while allowing access to others.
To exclude MCP servers:
- Navigate to the Org, Team, or UserProfile detail view in the Django Admin
- In the “Excluded MCP Servers” section, select the servers you want to exclude
- Save the changes
When an MCP server is excluded:
- Requests to that server return a 404 error
- The server is effectively unavailable to users in that scope
MCP Server Exclusion Hierarchy
MCP server exclusions follow the same hierarchical pattern as model exclusions:
- For User Tokens: UserProfile → Org → Global Settings
- For Service Account Tokens: Team → Org → Global Settings
The merge_mcp_server_exclusion_lists field works identically to merge_exclusion_lists:
- When enabled (default), the exclusion list includes servers from the current level plus all higher levels
- When disabled, only the current level’s exclusions apply, stopping the upward merge
Example:
A Team excludes ["server-a"] with merge enabled; its Org excludes ["server-b"] with merge disabled; global settings exclude ["server-c"]. Service accounts in that Team would have an effective exclusion list of ["server-a", "server-b"]—the Org’s merge disabled prevents the global server-c from being included.
You can configure the global default MCP server exclusion list in settings.py using the AQUEDUCT_DEFAULT_MCP_SERVER_EXCLUSION_LIST setting (defaults to an empty list).
MCP Server Configuration
MCP servers are configured through a JSON file referenced in settings.py via MCP_CONFIG_FILE_PATH (defaults to “mcp.json”). Each server configuration includes:
- type: Transport type (e.g., “streamable-http”)
- url: Server endpoint URL
- description: Server description
- tags: Categories for organization
Example configuration:
{
"mcpServers": {
"test-server": {
"type": "streamable-http",
"url": "http://localhost:3001/mcp",
"description": "For Streamable HTTP connections",
"tags": ["development", "testing"]
}
}
}